Best Chapter 4 Accounting For Merchandising Operations

We explain how reporting merchandising activities differs from reporting service activities.
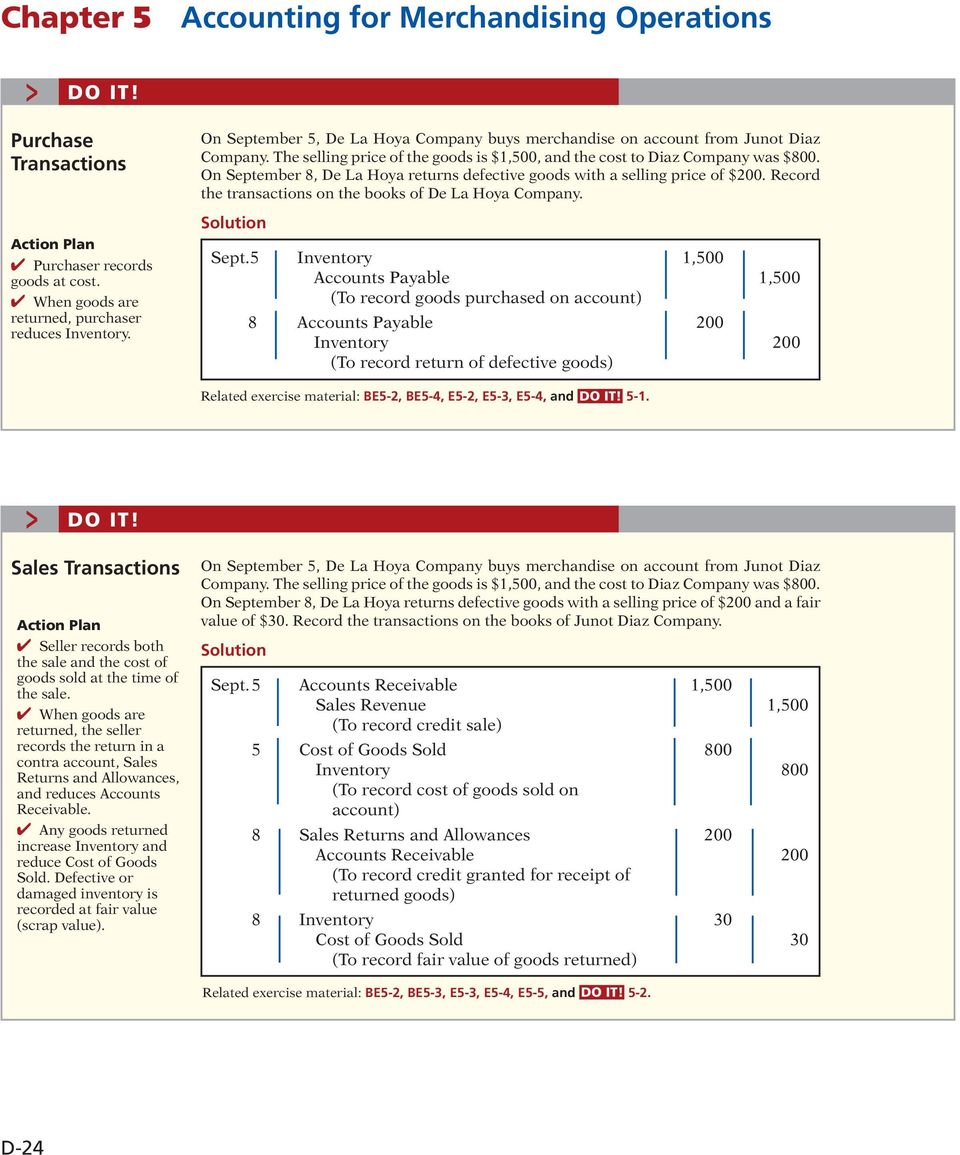
Chapter 4 accounting for merchandising operations. On September 12 Vander Company sold merchandise in the amount of 6600 to Jepson Company with credit terms of 310 n30. Chapter 4 PPT-1pptx - Accounting for Merchandising. This preview shows page 1 - 11 out of 46 pages.
Accounting for merchandising operations learning objectives 1. Adjusting Entries and Closing Entries 23. Chapter 4 Accounting for Merchandising Operations MERCHANDISING ACTIVITIES Merchandise consists of products also called goods that a company acquires to resell to customers 1.
Explain the recording of purchases under a perpetual inventory system. The cost of the items sold is 4800. Accounting For Merchandising Operations 4 Required Information The Following Information Applies To The Questions Displayed Below Part 3 Of 6 Santana Rey Created Business Solutions On October 1 2017.
Accounting firms law firms and plumbing services. WEYGANDT FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING IFRS Edition 2e CHAPTER 5 ACCOUNTING FOR MERCHANDISING OPERATIONS Number LO BT Difficulty Time min BE1 1 AP Simple 46 BE2 2 3 AP Simple 24 BE3 3 AP Simple 68 BE4 2 AP Simple 68 BE5 4 AP Simple 12 BE6 4 AP Simple 24 BE7 5 AP Simple 24 BE8 5 C Simple 46. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter you should be able to.
Sales - Sales Discount - Sales returns and Allowances Net Sales Net Sales - Cost of good sold Gross profit Gross profit -. To Accommodate The Growth The Accounting System Is Modified To Set. The income measurement process in a merchandising company can be summarized as follows.
Purchase returns - To record a return of merchandise purchased on account. Chapter 4 Learning Objectives 2 CONCEPTUAL C1 Describe merchandising activities and identify income components for a merchandising company. 4 Each of the required steps in the accounting cycle applies to a merchandising company.