Supreme Balance Sheet Assertions Balance Sheet Definition And Example
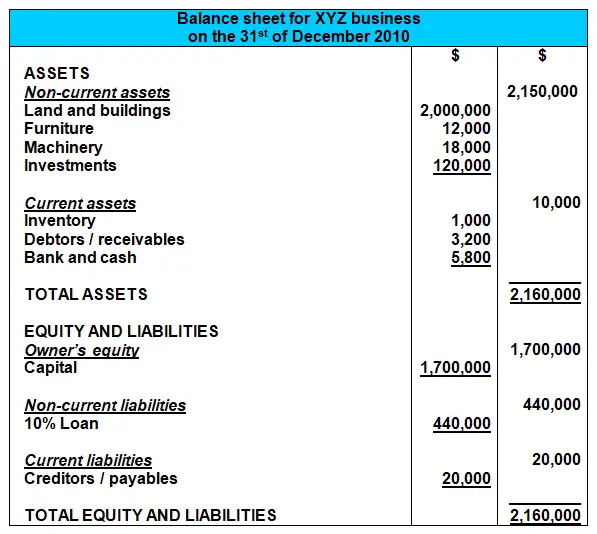
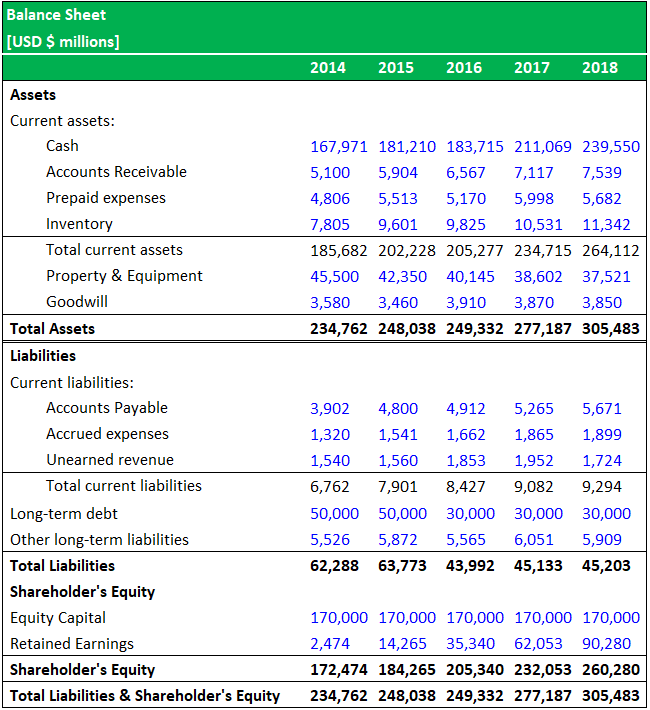
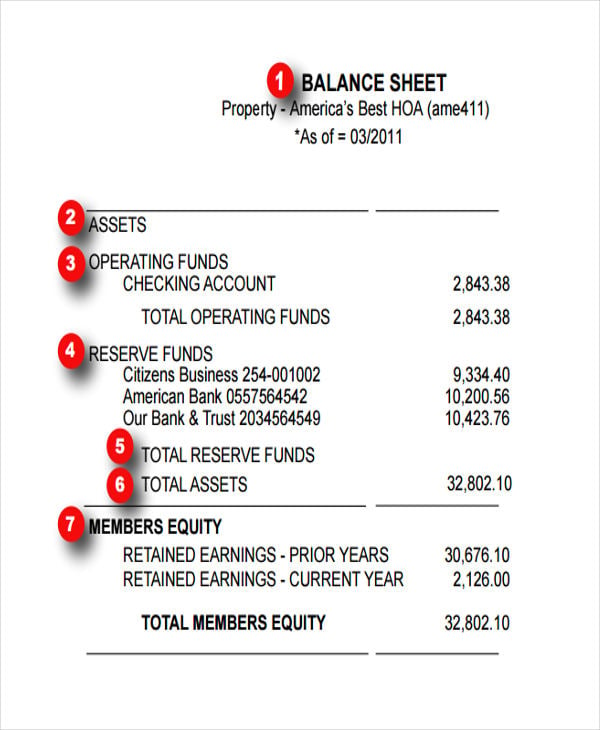
A balance sheet is a statement of the financial position of a business that lists the assets liabilities and owners equity at a particular point in time.
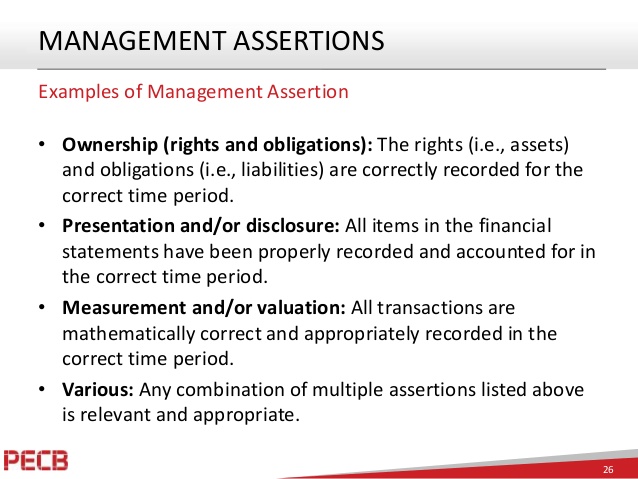
Balance sheet assertions balance sheet definition and example. The assertion is that recorded business transactions actually took place. Balance sheet or statement of financial position has 4 assertions. Let me explain all the balance sheet assertions through an example.
A balance sheet gives a snapshot of your financials at a particular moment incorporating every journal entry since your company launched. Aug 24 2020 Bookkeeping by Adam Hill Examples include surprise cash counts taking inventory review and approval of accounting work internal audits peer reviews and enforcement of job descriptions and expectations. The Balance Sheet is a statement that shows the financial position of the business.
A balance sheet gives a statement of a businesss assets liabilities and shareholders equity at a specific point in time. This assertion is very closely related to the occurrence assertion for transactions. Some assertions may apply to some items but not to others.
Definition of balance sheet. In the audit of inventory existence or occurrence assertion tests whether the inventory on balance sheet actual exists and whether inventory transactions actually took place. A balance sheet tells you a businesss worth at a given time so you can better understand its financial position.
The balance sheet is one of the three main financial statements along with the income statement and cash flow statement. The company has the right to control and use its assets and have obligations to pay its. Account balance assertions apply to the balance sheet items such as assets liabilities and shareholders equity.
These assertions apply to the balance sheet and income statement both of which are critical financial statements. They offer a snapshot of what your business owns and what it owes as well as the amount invested by its owners reported on a single day. This is the main principle behind the balance sheet audit approach.